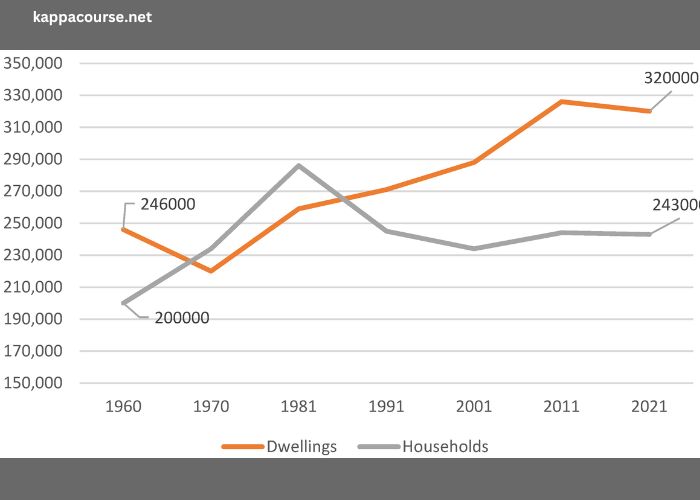
The world of cryptocurrency, especially Bitcoin, is deeply intertwined with the ideas of open-source software programs. Bitcoin’s genesis may be traced again to a whitepaper posted by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, who laid out the blueprint for a decentralized virtual currency. What was observed was the discharge of the Bitcoin software as open supply, allowing all people to view, alter, and contribute to its code. So, if you are starting to invest in crypto trading, you may visit Go quantumator.org.
The Essence of Open Source Software
Open supply software (OSS) is characterized by its publicly reachable code, which anybody can look into, adjust, and enhance. This approach contrasts with a proprietary software program, in which the supply code is saved exclusively and managed by a single entity. OSS fosters a collaborative environment in which builders from around the sector can make contributions to a task, driving innovation and improvement.
Bitcoin: An Open-Source Pioneer
Bitcoin was one of the first essential implementations of blockchain technology and decentralized virtual foreign money. The decision to release Bitcoin as an open supply turned pivotal for several reasons:
Transparency and Trust:
By making the code publicly accessible, Satoshi Nakamoto ensured that all and sundry should audit the machine. This transparency is crucial for building belief in a system that targets replacing traditional economic intermediaries.
Collaborative Improvement:
Open source allows a global network of builders to make contributions to the challenge. This has brought about continuous improvements in the protection, capability, and scalability of the Bitcoin community.
Decentralization:
The ethos of decentralization is at the heart of Bitcoin. Open-source software programs align perfectly with this precept, as they prevent any unmarried entity from having control over the codebase.
Collaborative Development in Bitcoin
The collaborative nature of open-source improvement has been a driving force behind Bitcoin’s boom and resilience. Several key factors spotlight this collaborative development:
Core Development Team
Bitcoin’s core development crew includes developers from around the sector who make voluntary contributions to the project. This team oversees essential updates and enhancements, making sure that Bitcoin stays secure and green. The decentralized nature of the group prevents any unmarried point of failure and distributes the decision-making process.
Community Contributions
Beyond the middle team, limitless developers and fans make contributions to Bitcoin’s improvement. Contributions range from code improvements and malicious program fixes to providing and imposing new capabilities. This huge participation facilitates identifying and coping with troubles more quickly than a centralized team could.
Peer review and auditing
Open supply tasks benefit from peer assessment and auditing, which complements the excellent quality and security of the software program. In the case of Bitcoin, which means any proposed modifications are scrutinized with the aid of a huge network of experts earlier than being common, This rigorous review system enables us to preserve the integrity and reliability of the Bitcoin network.
BIPs (Bitcoin Improvement Proposals)
Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs) are a proper mechanism for providing adjustments to the Bitcoin protocol. BIPs are submitted through developers, undergo big dialogue, and are evaluated via the network. This manner ensures that any changes are thoroughly vetted and debated before being implemented, preserving the stability and safety of the network.
The Broader Impact of Open Source in Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin’s achievement has stimulated the wider cryptocurrency space to include open-source principles. Many blockchain tasks and cryptocurrencies are developed as open supply, fostering innovation and collaboration. Some fantastic examples include:
Ethereum
Ethereum, the second-biggest cryptocurrency via marketplace capitalization, is an open supply platform for decentralized applications (dApps) and clever contracts. Its development network is colorful and active, contributing to the continuous evolution of the platform.
Litecoin
Litecoin, frequently known as the silver to Bitcoin’s gold, is any other open-supply cryptocurrency. It was created by Charlie Lee by making changes to Bitcoin’s codebase, demonstrating how open supply can facilitate the creation of the latest initiatives.
Monero
Monero is an open-source cryptocurrency centered on privacy and protection. Its development community emphasizes transparency and collaboration, with participants from around the world improving its privacy capabilities.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The DeFi movement, which seeks to recreate conventional financial structures through the use of blockchain, relies closely on open-source development. Platforms like Uniswap, Compound, and Aave are all open source, making allowances for network-driven innovation and development.
Conclusion
Bitcoin and open-source software are inextricably related, with the latter playing a vital role in the former’s improvement and achievement. The collaborative nature of open source has enabled Bitcoin to adapt and enhance continuously, supported by an international community of developers and enthusiasts. This model has not only fashioned Bitcoin but has also motivated the broader cryptocurrency space, fostering innovation and decentralization. By addressing demanding situations related to investment, governance, and safety, the open supply network can force ahead the evolution of digital currencies and the blockchain era, ensuring that they continue to be robust, obvious, and inclusive.